티스토리 뷰
[NoSQL] MongoDB 탐구하기
회사에서 MongoDB를 사용하는 프로젝트가 있다.
사실 저장, 수정, 조회, 삭제 api 활용이 전부인지라.. 그냥.. 사용하고 있었다.
It's just... 😲 😨 😱
.
지금은 MongoDB를 효율적으로 사용하기 위해 몽고와 친해져야 할 때이다.🤭
🍬 🍭을 챙겨서 몽고의 마음을 사로잡아보자.
.
참고로, MongoDB와 이제 막 친해지기 위한 단계로 깊은 내용은 담지 않았다...😢
깊은 내용은 몽고와 더 친해지면 준비할 예정이다.🧐
.
참고로, kciter 님의 MongoDB 이해하기 글이 많은 도움이 되었다.
kciter 님 글과 MongoDB Manual을 참고하여 간략하게 정리해보았고, 자세한 설명은 각 링크를 참고해보면 좋을 것 같다.
NoSQL
Not Only SQL
- 관계형 데이터베이스(RDBMS)와 달리
SQL을 사용하지 않는 데이터베이스 - MongoDB, Redis, HBase ...
NoSQL은 RDBMS의 한계를 개선
- 수평 확장 가능한 분산 시스템
- Schema-less
- 완화된 ACID
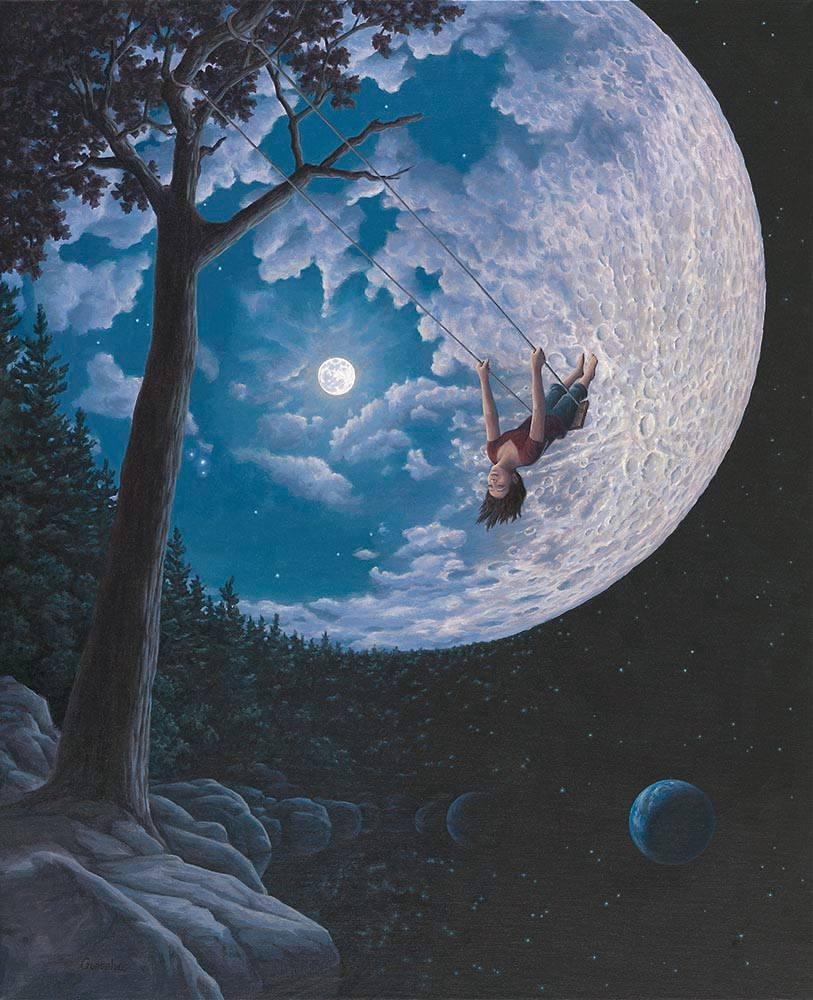
Document
MongoDB는 Document 기반 데이터베이스이다.
- What's the Documents?
- 데이터 레코드를 BSON 문서로 저장
- 필드 및 값 쌍으로 구성
{ field1: value1, field2: value2, ... fieldN: valueN } - 입력 가능한 value data types : BSON data types
- ...
.
MongoDB 계층 : Database > Collection > Document > Field
Document 기반 데이터베이스는 데이터 구조가 자유로움
- BSON으로 데이터가 쌓이므로 Array, Nested 한 데이터를 쉽게 저장 가능
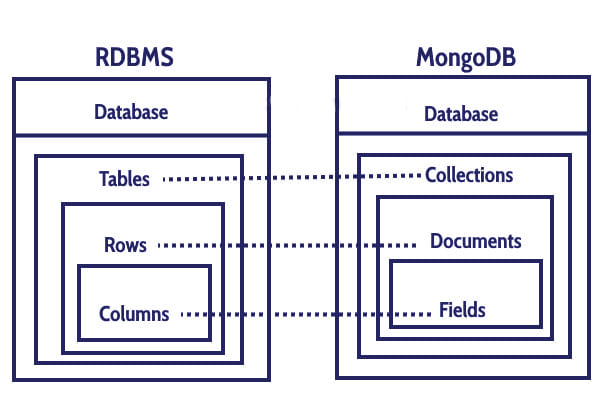
ObjectId
ObjectId는 RDBMS의Primary Key와 같이 고유한 키를 의미- 삽입된 문서가
_id를 생략하면 MongoDB driver가 자동으로 필드에 대한 ObjectId를 생성
데이터 조작
- NoSQL은 SQL을 사용하지 않고 별도로 제공하는
API를 통해 데이터 조작
Insert
// Insert Basic
db.inventory.insertOne(
{ "item" : "canvas",
"qty" : 100,
"tags" : ["cotton"],
"size" : { "h" : 28, "w" : 35.5, "uom" : "cm" }
}
)
// Insert Many
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": { "h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "A" },
{ "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "status": "A" },
{ "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "status": "D" },
{ "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": { "h": 22.85, "w": 30, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "D" },
{ "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": { "h": 10, "w": 15.25, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "A" }
]);Read
// Read All Documents
db.inventory.find({})
// Read With Queries
db.inventory.find( { status: "D" } )
// Read Using Operators and Compound Queries
// operator
db.inventory.find( { "size.h": { $lt: 15 } } )
// AND
db.inventory.find( { status: "A", qty: { $lt: 30 } } )
// OR
db.inventory.find( { $or: [ { status: "A" }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] } )
// AND & OR
myCursor = db.inventory.find( {
status: "A",
$or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: /^p/ } ]
} )Update
// Update a Single document
db.inventory.updateOne(
{ "item" : "paper" }, // specifies the document to update
{
$set: { "size.uom" : "cm", "status" : "P" },
$currentDate: { "lastModified": true }
}
)
// Update Multiple documents
db.inventory.updateMany(
{ "qty" : { $lt: 50 } }, // specifies the documents to update
{
$set: { "size.uom" : "cm", "status": "P" },
$currentDate : { "lastModified": true }
}
)Delete
// Delete a single document.
db.inventory.deleteOne(
{ "status": "D" } // specifies the document to delete
)
// Delete multiple documents.
db.inventory.deleteMany(
{ "status" : "A" } // specifies the documents to delete
)BASE
ACID와 대립되는 개념
(Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability)
(원자성, 일관성, 격리성, 지속성)
.
BASE는 일관성을 어느 정도 포기하고 가용성을 우선시
- Basically, Avaliable
(가용성)- 기본적으로 언제든지 사용 가능
- Soft state
(독립성)- 외부의 개입이 없어도 정보가 변경될 수 있음
- 네트워크 파티션 등 문제가 발생되어 일관성이 유지되지 않는 경우 일관성을 위해 데이터를 자동으로 수정
- Eventually consistent
(일관성)- 일시적으로 일관적이지 않은 상태가 되어도 일정 시간 후 일관적인 상태가 되어야 함
- 장애 발생 시 일관성을 유지하기 위한 이벤트를 발생
분산 시스템
MongoDB와 PACELC
- MongoDB는
PA / EC시스템이므로 네트워크 파티션 상황일 때 가용성을 더 우선시하고 평상시엔 일관성을 우선시
MongoDB Replica Set
- MongoDB는 클러스터 구성을 위한 가장 간단한 방법으로 Replica Set 이용
- Sharded Cluster 구성도 가능
P-S-S
- 하나의 Primary와 여러 개의 Secondary로 이루어진 Replica Set
- Primary가 죽을 경우 투표를 통해 남은 Secondary 중 새로운 Primary를 선출
- 여기서 Secondary가 하나만 남았다면 새로운 Primary를 선출할 수 없어 서버 장애 발생
P-S-A
- 하나의 Primary와 Arbiter 그리고 여러 개의 Secondary로 이루어진 Replica Set
- Primary가 죽을 경우 Arbiter가 Secondary와 함께 투표해서 Secondary 중 새로운 Primary를 선출
- Secondary가 하나만 남았더라도 Arbiter가 남아있어서 남은 Secondary를 Primary로 선출할 수 있어서 정상적으로 서비스 동작
MongoDB Pattern
MongoDB는 Document 방식을 사용하기 때문에 RDBMS와는 다른 방식으로 모델링이 필요
Model Tree Structure
같은 Collection에서 데이터가 서로를 참조하는 Tree 구조를 가지고 있을 때 사용할 수 있는 패턴

- 부모 Document를 바로 찾아야 하는 경우
- 하위 트리를 모두 찾아야 하는 경우엔 부적합
db.categories.insertMany( [
{ _id: "MongoDB", parent: "Databases" },
{ _id: "dbm", parent: "Databases" },
{ _id: "Databases", parent: "Programming" },
{ _id: "Languages", parent: "Programming" },
{ _id: "Programming", parent: "Books" },
{ _id: "Books", parent: null }
] )- 자식 Document를 바로 찾아야 하는 경우
- 부모 Document도 찾을 수 있지만 Parent References보다 탐색 성능 저하
db.categories.insertMany( [
{ _id: "MongoDB", children: [] },
{ _id: "dbm", children: [] },
{ _id: "Databases", children: [ "MongoDB", "dbm" ] },
{ _id: "Languages", children: [] },
{ _id: "Programming", children: [ "Databases", "Languages" ] },
{ _id: "Books", children: [ "Programming" ] }
] )- 조상 Document를 바로 알 수 있어야 하는 경우와 자식 Document를 모두 찾아야 하는 경우
db.categories.insertMany( [
{ _id: "MongoDB", ancestors: [ "Books", "Programming", "Databases" ], parent: "Databases" },
{ _id: "dbm", ancestors: [ "Books", "Programming", "Databases" ], parent: "Databases" },
{ _id: "Databases", ancestors: [ "Books", "Programming" ], parent: "Programming" },
{ _id: "Languages", ancestors: [ "Books", "Programming" ], parent: "Programming" },
{ _id: "Programming", ancestors: [ "Books" ], parent: "Books" },
{ _id: "Books", ancestors: [ ], parent: null }
] )- Array of Ancestors와 유사
- Array 타입이 아닌 String 타입을 이용하는데, 정규식을 이용하여 하위 항목을 탐색
db.categories.insertMany( [
{ _id: "Books", path: null },
{ _id: "Programming", path: ",Books," },
{ _id: "Databases", path: ",Books,Programming," },
{ _id: "Languages", path: ",Books,Programming," },
{ _id: "MongoDB", path: ",Books,Programming,Databases," },
{ _id: "dbm", path: ",Books,Programming,Databases," }
] )- 하위 트리를 찾는데 가장 빠르고 효율적인 방법
- 구조가 변경되는 경우 다시 데이터 번호를 매기는데 비용이 크기 때문에 데이터가 추가, 삭제, 변경되지 않는 정적인 구조에 적합
db.categories.insertMany( [
{ _id: "Books", parent: 0, left: 1, right: 12 },
{ _id: "Programming", parent: "Books", left: 2, right: 11 },
{ _id: "Languages", parent: "Programming", left: 3, right: 4 },
{ _id: "Databases", parent: "Programming", left: 5, right: 10 },
{ _id: "MongoDB", parent: "Databases", left: 6, right: 7 },
{ _id: "dbm", parent: "Databases", left: 8, right: 9 }
] )Model Relationships
Model Relationships Between Documents
Reference
Foreign Key처럼 키를 이용하여 참조1:1
// patron document
{
_id: "joe",
name: "Joe Bookreader"
}
// address document
{
patron_id: "joe", // reference to patron document
street: "123 Fake Street",
city: "Faketon",
state: "MA",
zip: "12345"
}1:N
// patron document
{
_id: "joe",
name: "Joe Bookreader"
}
// address documents
{
patron_id: "joe", // reference to patron document
street: "123 Fake Street",
city: "Faketon",
state: "MA",
zip: "12345"
}
{
patron_id: "joe",
street: "1 Some Other Street",
city: "Boston",
state: "MA",
zip: "12345"
}Embed
- Document에 Object로 데이터를 포함
1:1
{
_id: "joe",
name: "Joe Bookreader",
address: { //embed the address data in the patron data
street: "123 Fake Street",
city: "Faketon",
state: "MA",
zip: "12345"
}
}1:N
{
"_id": "joe",
"name": "Joe Bookreader",
"addresses": [ //embed the address data entities in the patron data
{
"street": "123 Fake Street",
"city": "Faketon",
"state": "MA",
"zip": "12345"
},
{
"street": "1 Some Other Street",
"city": "Boston",
"state": "MA",
"zip": "12345"
}
]
}Modeling Pattern
MongoDB는 Subquery, Join과 같은 기능을 제공해주지 않는다.
.
Collection의 참조 성능을 고려하고, 데이터를 단순화하기 위해 모델링 패턴을 이용할 수 있다.
.
모델링 패턴을 탐구하며 NoSQL은 최대한 단순하면서 많은 데이터에 적용, RDBMS는 복잡하면서 무결성이 중요한 데이터에 적용하는 것이 적합하다는 말에 공감할 수 있었다.
.
Top 6 Pattern..
- 동일한 필드를 묶어서
인덱싱 수를 줄이는 패턴 - 하나의 필드에 묶어서 인덱스를 관리
Before
{
title: "Star Wars",
director: "George Lucas",
...
release_US: ISODate("1977-05-20T01:00:00+01:00"),
release_France: ISODate("1977-10-19T01:00:00+01:00"),
release_Italy: ISODate("1977-10-20T01:00:00+01:00"),
release_UK: ISODate("1977-12-27T01:00:00+01:00"),
...
}
//Indexing
{release_US: 1}
{release_France: 1}
{release_Italy: 1}
...After
{
title: "Star Wars",
director: "George Lucas",
...
releases: [
{
location: "USA",
date: ISODate("1977-05-20T01:00:00+01:00")
},
{
location: "France",
date: ISODate("1977-10-19T01:00:00+01:00")
},
{
location: "Italy",
date: ISODate("1977-10-20T01:00:00+01:00")
},
{
location: "UK",
date: ISODate("1977-12-27T01:00:00+01:00")
},
...
],
...
}
//Indexing
{ "releases.location": 1, "releases.date": 1}- 서로 관계가 있는 Document에서
자주 사용되는 데이터를 저장해두는 패턴- 필요한 데이터를 연관된 Collection에서 일부분 Document에 저장
- MongoDB에선 성능을 위해 Join대신 쿼리를 두 번 날려 연관 데이터를 불러오는 방식을 많이 사용하는데, 데이터가 많아지고 참조가 자주 필요할수록 Extended Reference 패턴을 사용하는 것이 좋음

- 관계가 있는 Document 사이에
자주 사용되는 데이터를 부분적으로 Embed하는 패턴 - 정말 많이 쓰이는 패턴이지만 만일 데이터 수정이 발생한다면 양쪽 모두 수정이 필요

통계 결과를 데이터 삽입 시 미리 계산하여 저장하는 패턴- 집계 합수는 데이터가 많을수록 성능 저하가 있으므로 조금 오차가 발생해도 괜찮다면 Computed 패턴을 사용하는 것이 좋음
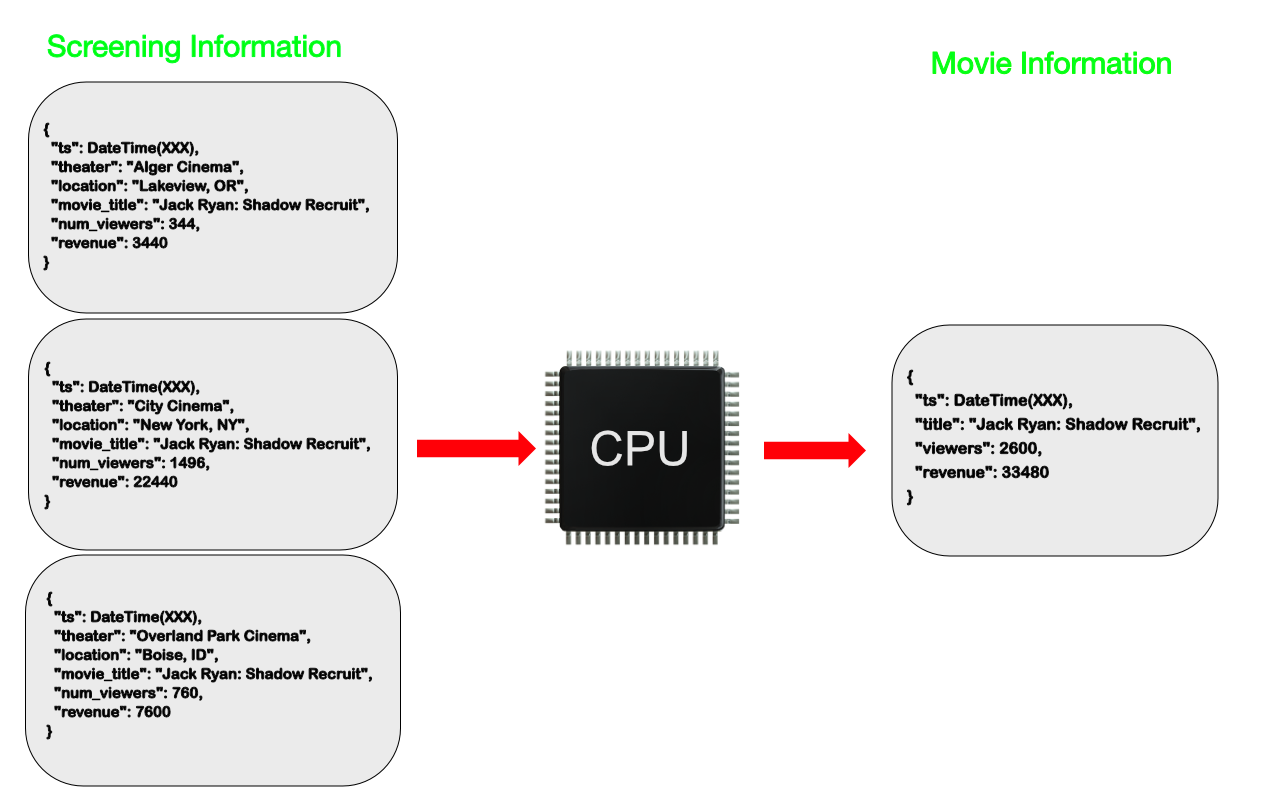
하나의 필드를 기준으로 Document를 묶는패턴- 실시간으로 데이터가 들어오는 시계열 데이터에 적합
- 단, BSON 크기 제한을 벗어나지 않도록
start_date,end_date를 이용하여 기준점을 가지는 것이 좋음
- 단, BSON 크기 제한을 벗어나지 않도록
- 필드 추가, 삭제에도 용이하고 인덱스 크기 절약 효과
Before
{
sensor_id: 12345,
timestamp: ISODate("2019-01-31T10:00:00.000Z"),
temperature: 40
}
{
sensor_id: 12345,
timestamp: ISODate("2019-01-31T10:01:00.000Z"),
temperature: 40
}
{
sensor_id: 12345,
timestamp: ISODate("2019-01-31T10:02:00.000Z"),
temperature: 41
}After
{
sensor_id: 12345,
start_date: ISODate("2019-01-31T10:00:00.000Z"),
end_date: ISODate("2019-01-31T10:59:59.000Z"),
measurements: [
{
timestamp: ISODate("2019-01-31T10:00:00.000Z"),
temperature: 40
},
{
timestamp: ISODate("2019-01-31T10:01:00.000Z"),
temperature: 40
},
...
{
timestamp: ISODate("2019-01-31T10:42:00.000Z"),
temperature: 42
}
],
transaction_count: 42,
sum_temperature: 2413
} Document에 버전 정보를 기록하는 패턴- 스키마가 변경될 경우 기존 데이터를 급하게 마이그레이션하지 않아도 된다.
schema_version필드를 활용하여 조회 후 천천히 마이그레이션 진행
Before
{
"_id": "<ObjectId>",
"name": "Darth Vader",
"home": "503-555-0100",
"work": "503-555-0110",
"mobile": "503-555-0120"
}After
{
"_id": "<ObjectId>",
"schema_version": "2",
"name": "Anakin Skywalker (Retired)",
"contact_method": [
{ "work": "503-555-0210" },
{ "mobile": "503-555-0220" },
{ "twitter": "@anakinskywalker" },
{ "skype": "AlwaysWithYou" }
]
}Referenvce
'Web' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Vue.js] Vue.js 시작하기 (0) | 2022.07.30 |
|---|---|
| Refactoring With IntelliJ Summary (0) | 2022.07.08 |
| [Message Queue] Apach Kafka 탐구하기 (0) | 2022.03.22 |
| [우아한 Tech] 우아한 ATDD (0) | 2022.02.22 |
| [IntelliJ] Spring, Maven, Tomcat Setting in Intranet (인트라넷 환경에서 설정) (0) | 2022.02.16 |
